- Products & services Products & services
- Resources ResourcesLearning
- Learning
- Identity University Get technical training to ensure a successful implementation
- Training paths Follow a role-based or product-based training path
- SailPoint professional certifications & credentials Advance your career or validate your identity security knowledge
- Training onboarding guide Make of the most of training with our step-by-step guide
- Training FAQs Find answers to common training questions
- Community Community
- Compass
- :
- Discuss
- :
- Community Wiki
- :
- IdentityIQ Wiki
- :
- Configuring IdentityIQ for use with SQL Server mirroring
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Content to Moderator
Configuring IdentityIQ for use with SQL Server mirroring
Configuring IdentityIQ for use with SQL Server mirroring
- Introduction
- SQL server configuration requirements
- Retrofitting IdentityIQ onto a mirroring pair
- Configuring schema-wide isolation
- Services standard build/build tools - Special considerations
Introduction
IdentityIQ has strict requirements for how its schema is configured on SQL Server environments. SQL Server databases handle row-level record mutual exclusion or "Locking" differently than other relational database systems. In SQL Server it is very easy to construct a set of queries across multiple tables that cause locking to be "contagious" or liberally applied to all objects involved in the query. This is not how IdentityIQ expects its relational database to apply locking semantics; IdentityIQ expect locking semantics similar to MySQL, Oracle, or DB2, all of which share a very similar and very restrictive structure for lock escalation at the relational database row and table level.
To support highly concurrent usage patterns, IdentityIQ's schema, as of the 7.0 release, requires the use of an isolation type called "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT". This mode of configuration enables a SQL Server database to have locking semantics similar to other relational database management systems, and is required for IdentityIQ to be able to safely execute parallelized and concurrent operations against a SQL Server database.
To address this, the IdentityIQ 7.0 release includes a modification to the DDL for SQL Server based databases that improves compatibility and performance on SQL Server based systems. This update also helps prevent deadlock conditions that have caused stack trace exceptions on previous versions of IdentityIQ. IdentityIQ 7.0 (and newer releases that will follow) now ship with the following statements in their SQL Server DDL files:
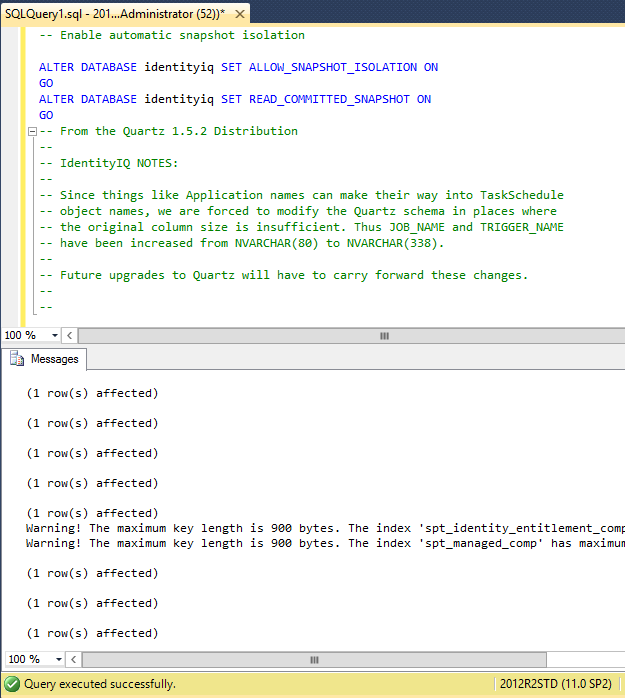
-- Enable automatic snapshot isolation
ALTER DATABASE identityiq SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON
GO
ALTER DATABASE identityiq SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON
GO
Most SQL Server databases are not configured for "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT" by default. While it may be obvious to some, it is worth nothing the above mentioned ALTER TABLE commands set isolation at the database level. Configuring SQL Server's "Mirroring" redundancy feature can be challenging for databases that require "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT" type isolation. The aim of this guide is to aid the deployment professional with the configuration of a SQL Server environment so that Mirroring's replication and safety benefits can co-exist with IdentityIQ's highly-parallelized performance features.
For more information about the particulars of SQL Server database locking semantics and how they compare and differ to other relational databases, please see the following KB article:
This MSDN article also has interesting background information on snapshot isolation:
SQL server configuration requirements
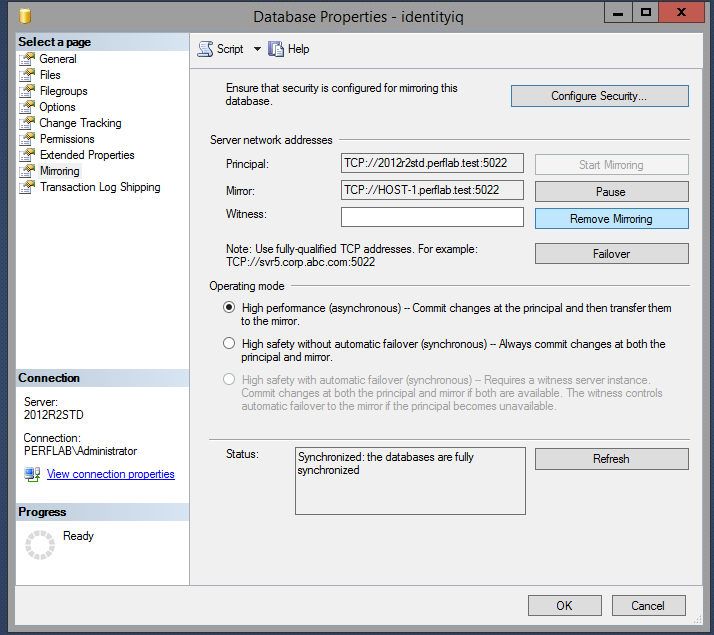
Only "High Performance" (asynchronous) mirroring mode is supported for use with IdentityIQ. The "High Safety" ("synchronous") mode of SQL Server mirroring is not a supported configuration for use with IdentityIQ. The "High Safety" mode causes SQL Server to operate in a 2-phase-commit type of operation that is shown as not-supported in the following guide: (Recommended IdentityIQ Deployment Architectures ).
IdentityIQ's back-end database can not be simply loaded into an already mirroring-enabled pair of servers due to its special locking configuration requirements. SQL Server will ignore the locking semantics requested when a new database is loaded onto an already existing pair or set of mirroring servers. Mirroring must be disabled during the initial loading of IdentityIQ's DDL in order for SQL Server to honor the "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT" parameter of IdentityIQ's DDL.
Retrofitting IdentityIQ onto a mirroring pair
To retrofit IdentityIQ onto a mirroring pair, you will apply a default snapshot setting schema-wide, where all connections are established and by defaulted assigned the "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT" isolation level (described below). This is the preferred method of configuration because it prevents connections from running transactions with isolation levels not compatible with IdentityIQ's locking needs.
Configuring schema-wide isolation
SQL Server mirroring is the technology that automates replication of the primary database to a backup database server. It is used by many, if not most, of the IdentityIQ installations that run enterprise environments on Microsoft SQL Server. SQL Server will not allow an administrator to alter the default isolation settings of a schema that is currently being replicated by SQL Server mirroring.
There is a workaround for this limitation of SQL Server; however, the procedure can be cumbersome. Installations that already have mirroring enabled, and would like to configure SQL Server to strictly default to using "READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT" isolation for connections made to IdentityIQ's database, should follow a procedure similar to the following when installing an IdentityIQ schema:
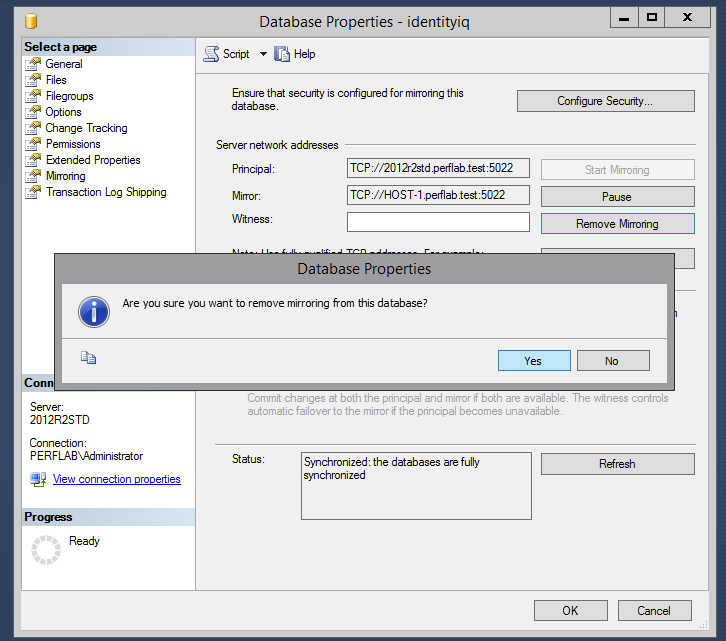
- Stop the SQL Server mirroring process between the two systems.
- Install the IdentityIQ database on the primary/master server. Take care to ensure the locking configuration statements are applied.
- Test connecting the IdentityIQ database from IIQ Console.
- Re-configure SQL Server mirroring to replicate the database to the standby side using "High Performance" mirroring.
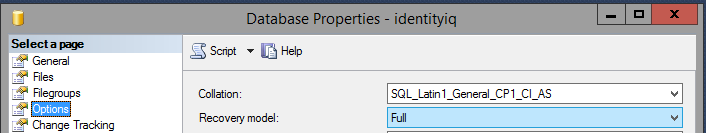
- Make sure the IIQ database is set to use the FULL recovery model.
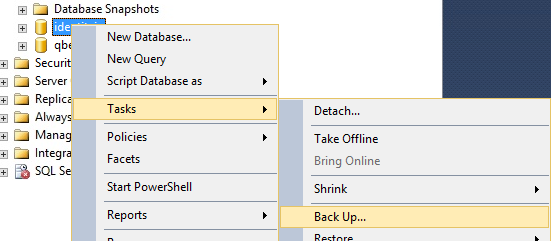
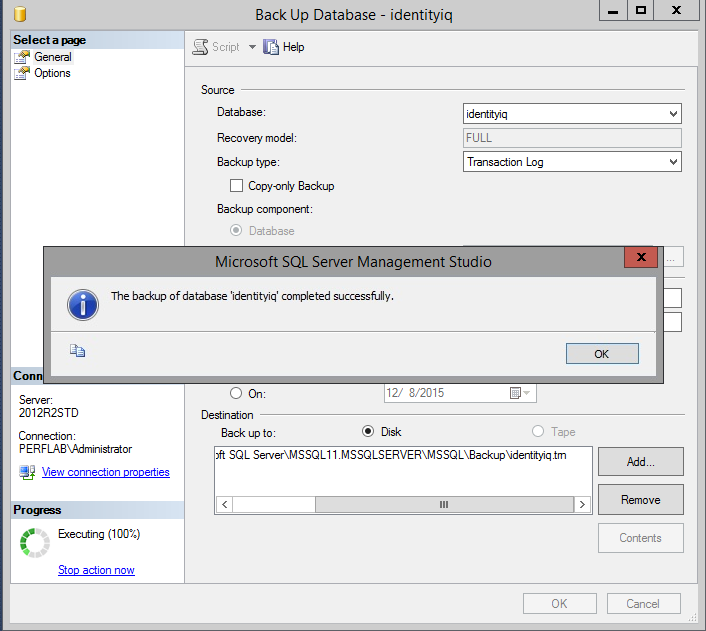
- Back up the IdentityIQ database and transaction logs.
- Start with the database
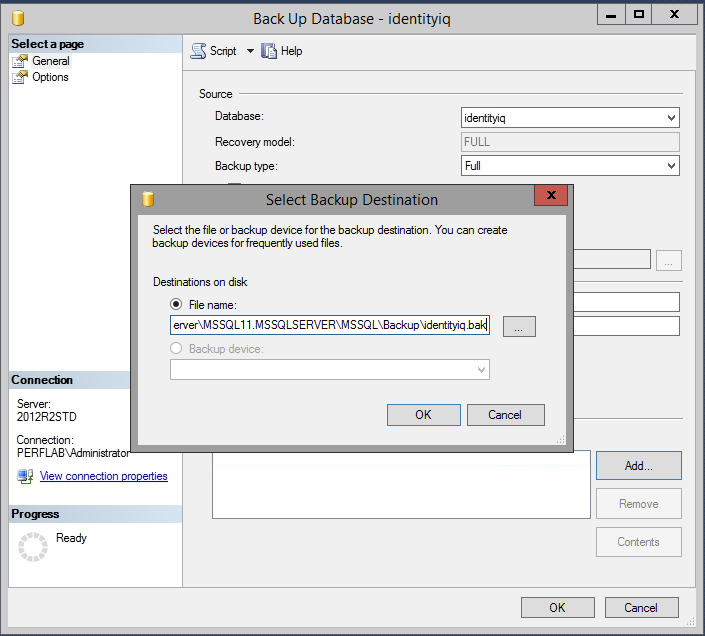
- Then back up the transaction log.
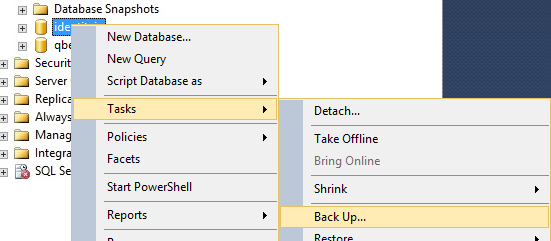
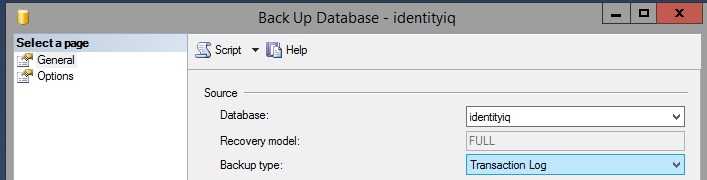
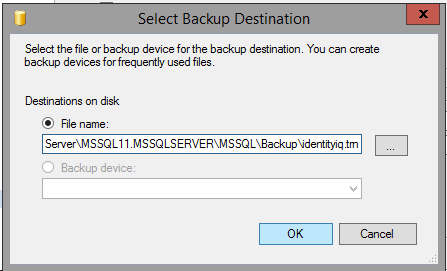
- Copy the database backup and transaction log files to the Mirroring (secondary) server, and restore them.
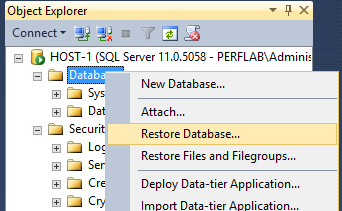
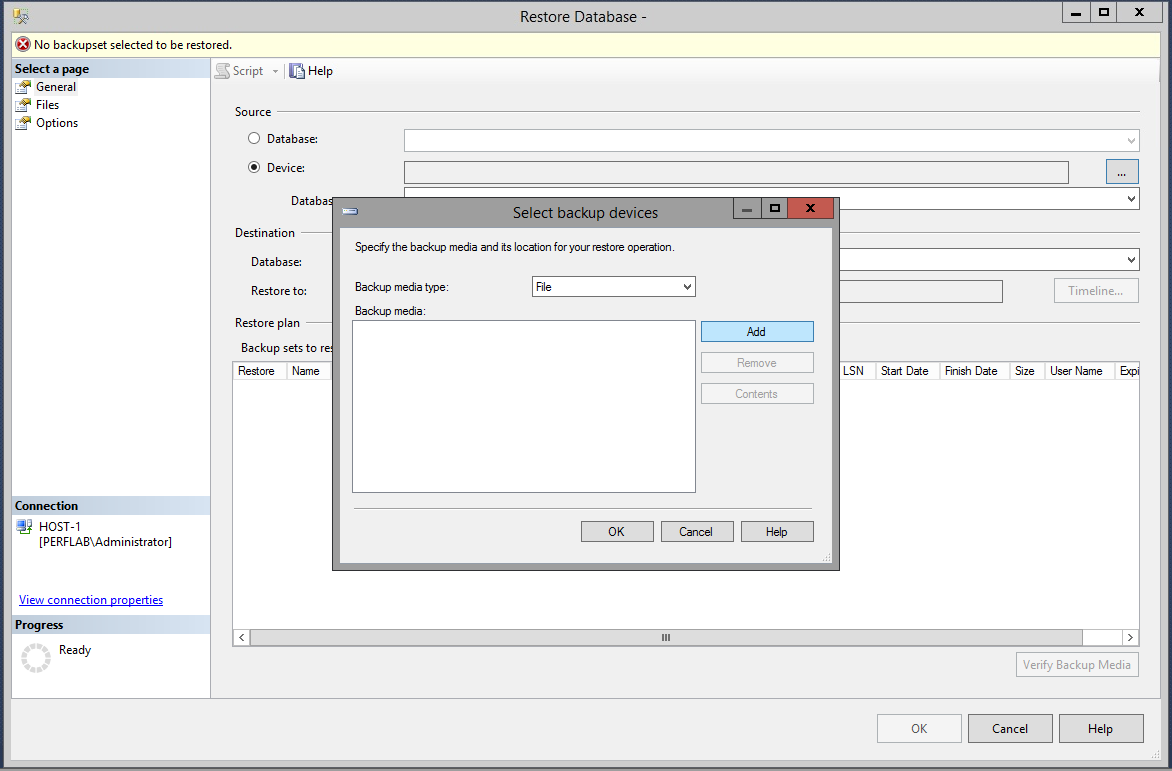
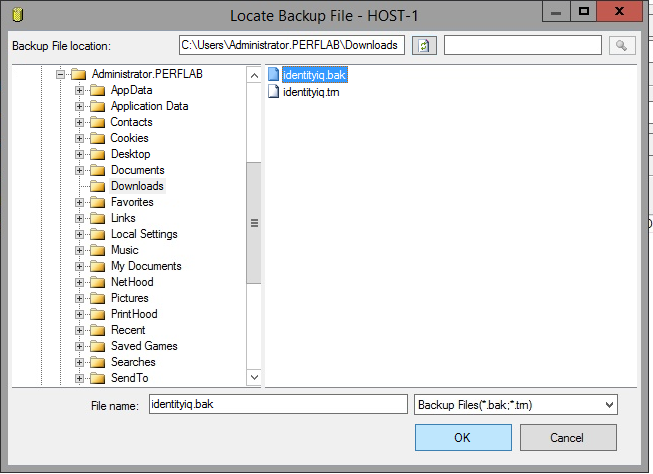
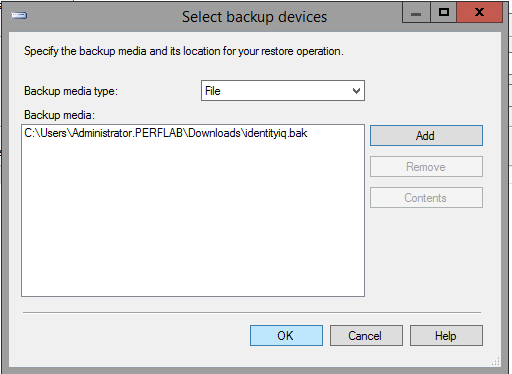
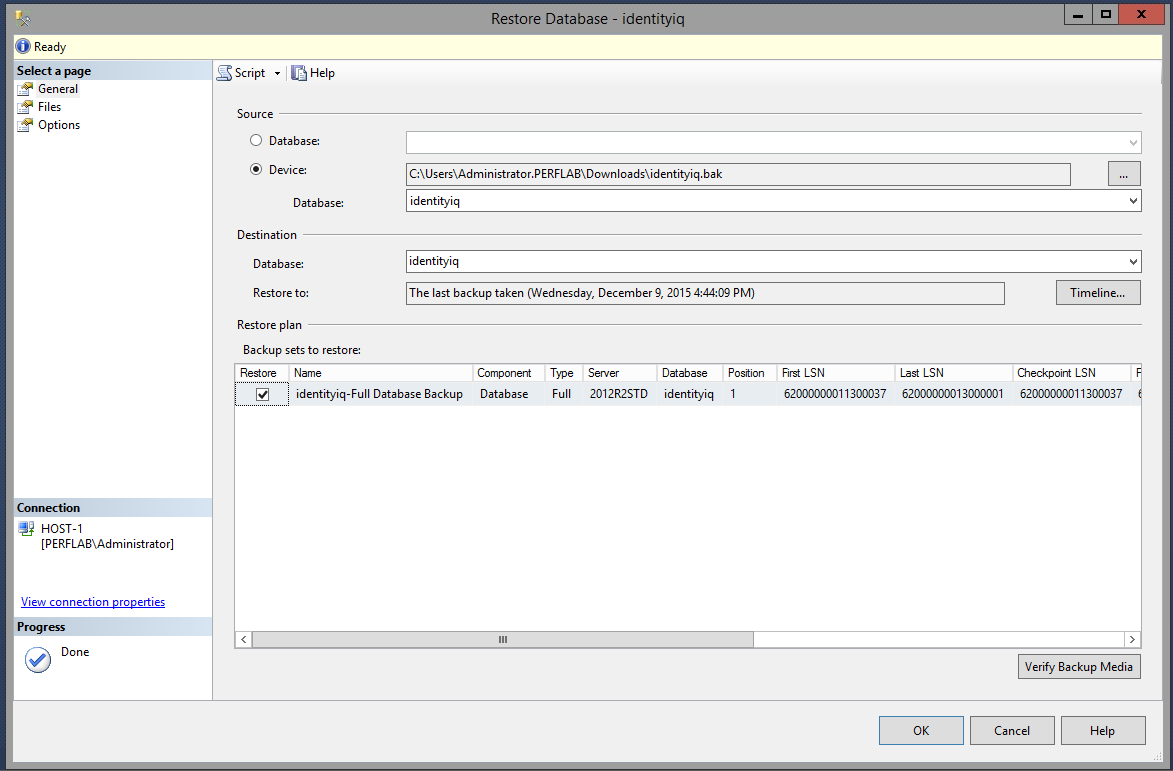
- go into "Options" and change Recovery state to "RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY".
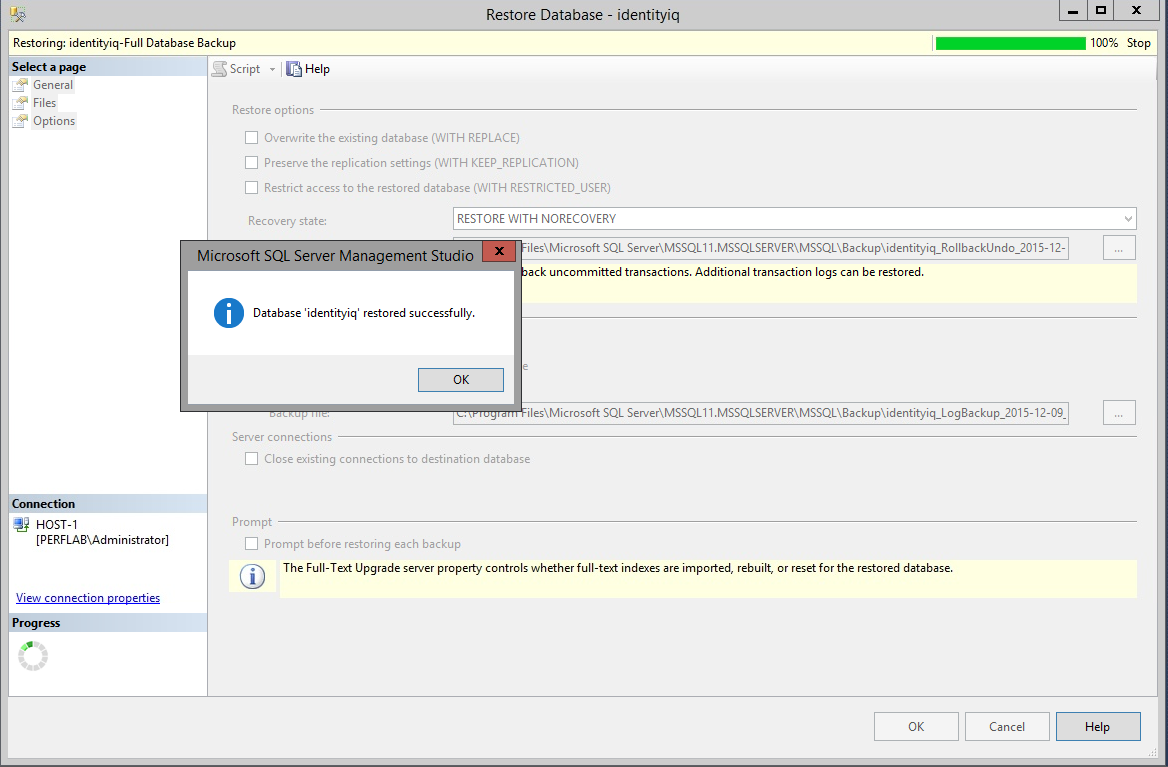
- Now do the same process with the backup transaction log from the principal server, making sure to change Recovery state to "RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY" as you did with the database backup.
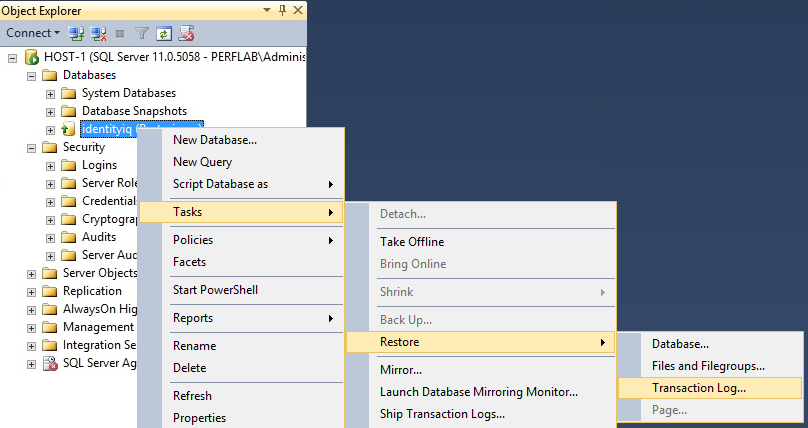
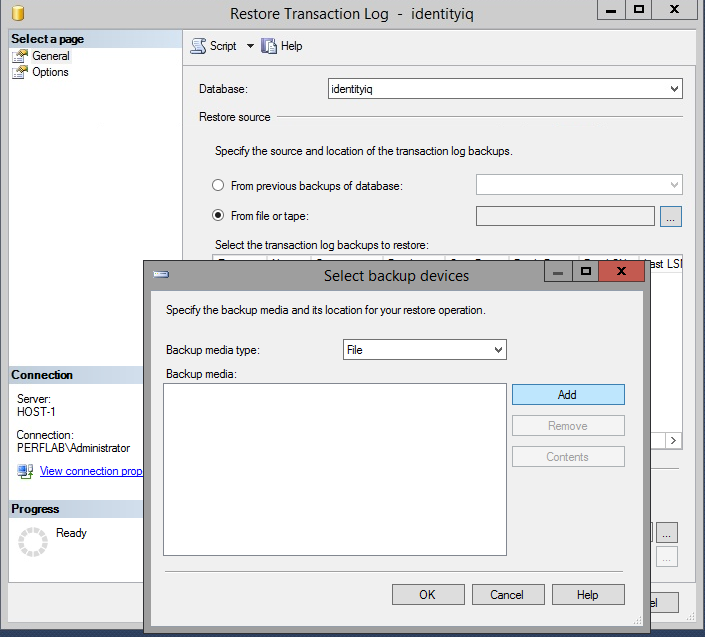
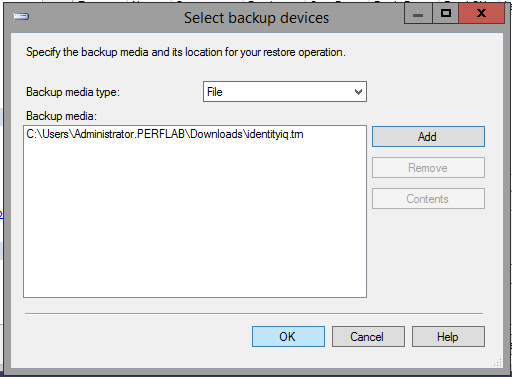
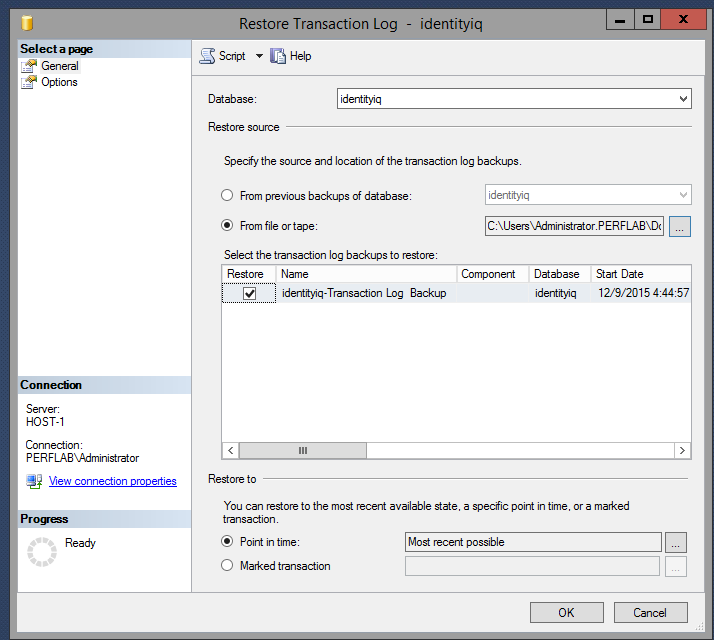
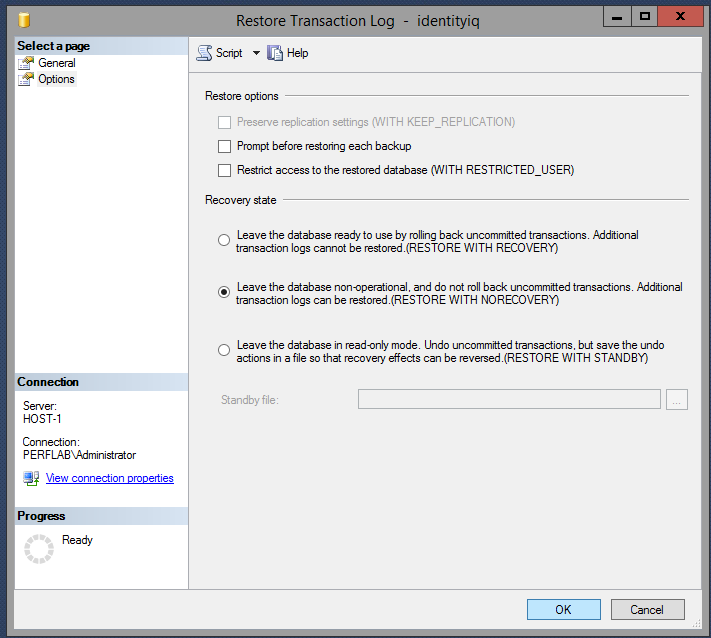
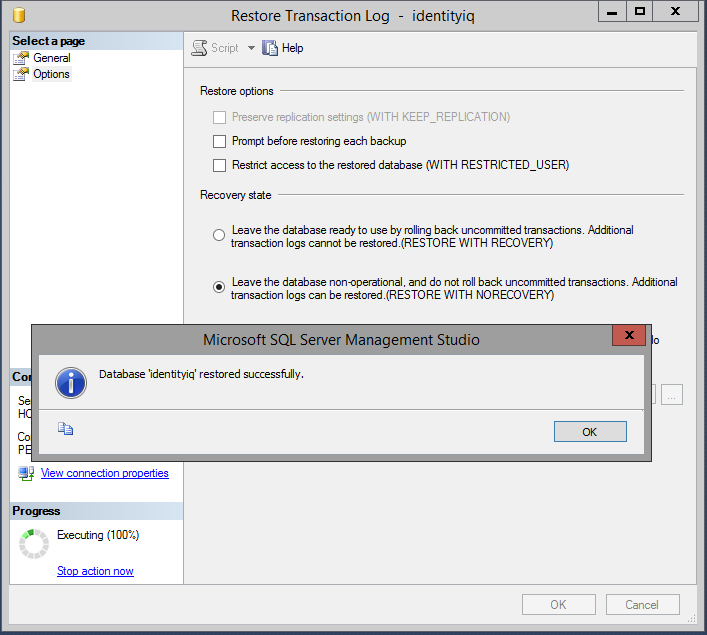
- Start with the database
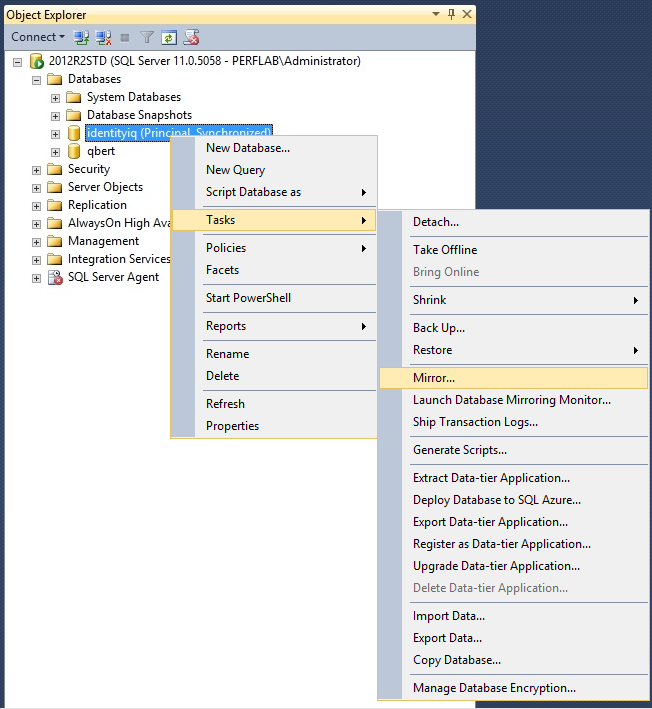
- Now, configure mirroring. Select the Principal and Mirror servers.
-
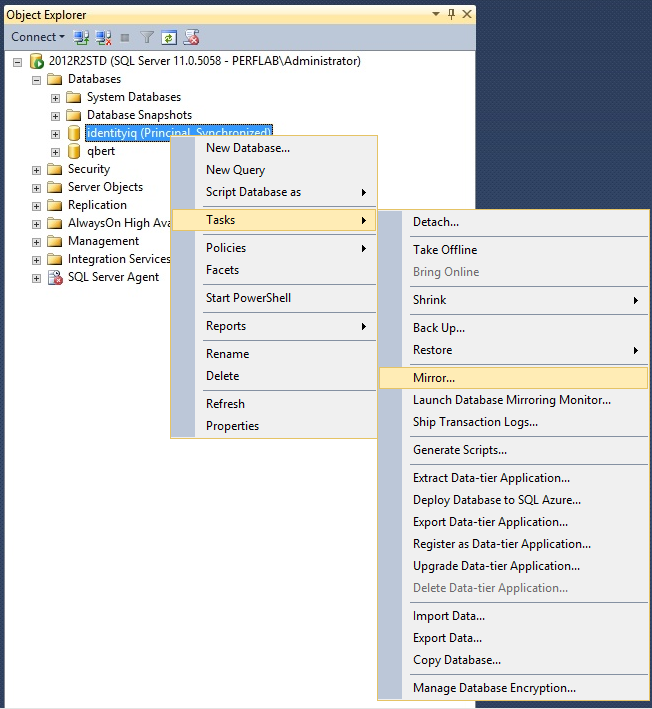
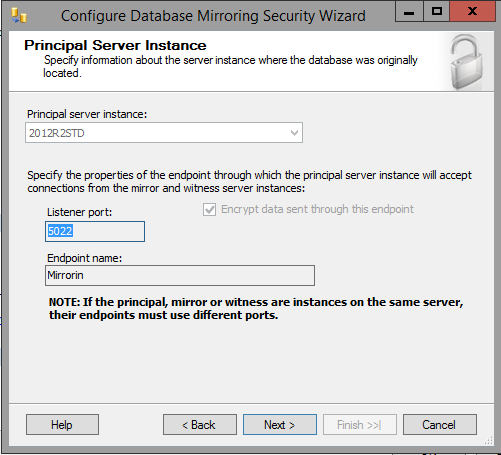
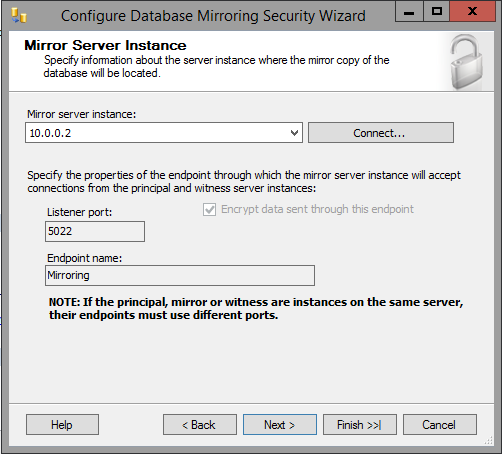
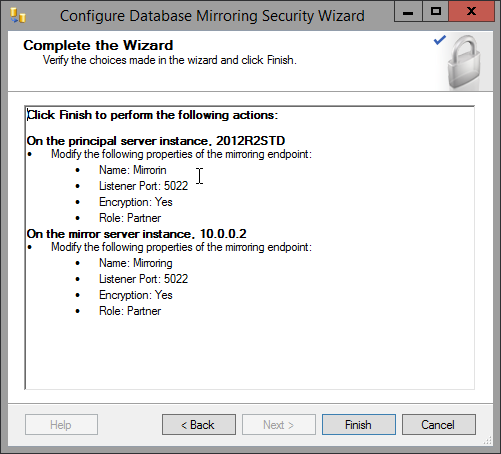
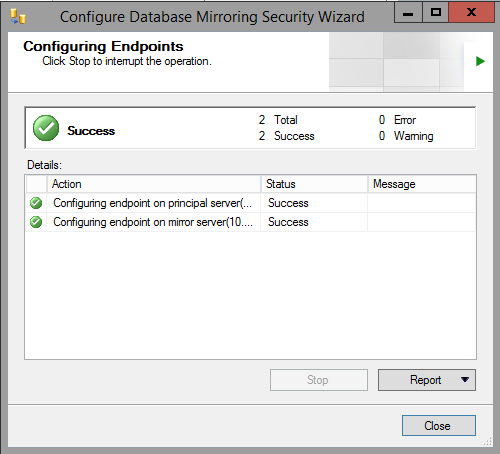
- Once the Security Wizard is complete, it will default to "High Safety (synchronous) operating mode". This mode is unsupported for IIQ, so click "Do Not Start Mirroring"
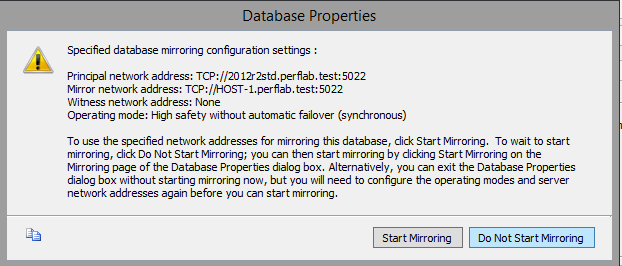
- Change the operating mode to "High Performance (asynchronous)".
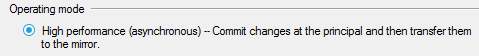
- Click "Start Mirroring".
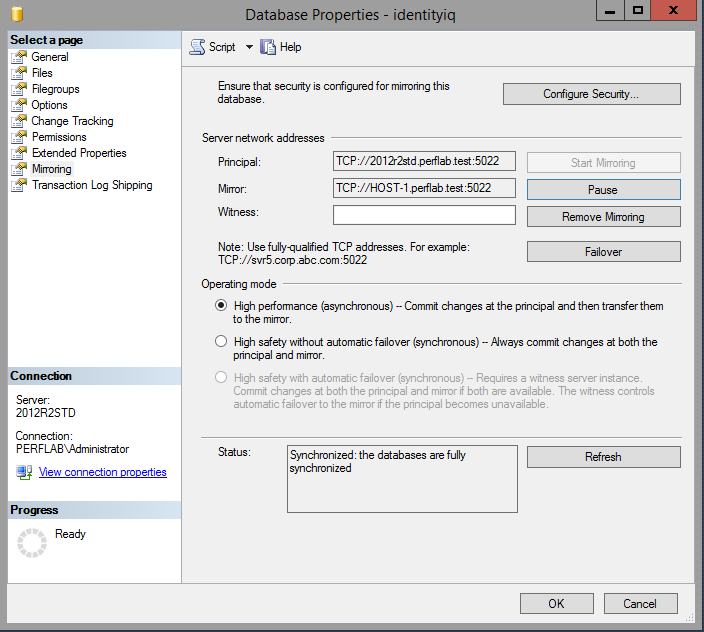
- Verify that the database on the principal server shows status "Principal, Synchronized".
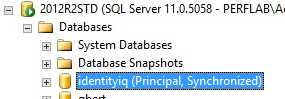
- Mirroring setup is complete!
-
- Test the configuration by running a heavily partitioned Identity Refresh or Account Aggregation task.
Services standard build/build tools - Special considerations
If you are using Services Standard Build (SSB) to build the database, you may still encounter deadlocks that the isolation changes described in this document are intended to address. This occurs because the SSB script executes the ALTER statements in a multi-statement transaction.
An error like this one may occur:
[sql] ALTER DATABASE iiq70 SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON
[sql] com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: ALTER DATABASE statement not allowed within multi-statement transaction.
These errors typically occur when you use a tool that executes the statements as one transaction; they don't occur when you use the script directly.
You can remedy this problem by running the ALTER statements separately after the tool has run. Alternatively, you can edit the SSB's build.dev.xml file (in the scripts directory),to insert the following on line 31:
autocommit="true"
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Content to Moderator
cathy.mallet
Is this setting also recommended for iiq versions prior to 7.0?
ALTER DATABASE identityiq SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON
GO
ALTER DATABASE identityiq SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON
GO
Also, I guess it is only required if replication is setup through mirroring and not using Always ON. Is that correct?
Thanks,
Gaurav
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Content to Moderator
Hi Gaurav -
I ran this by Jason S, who is the real expert. He said yes, this setting is recommended for pre-7.0 releases. He also said it should be added regardless of whether you are using mirroring or not; the tricky part is that if you are using mirroring, you have to disable that, apply the commands, then re-enable the mirroring.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Content to Moderator
Hi There,
I have a query were I would seek your suggestion/recommendations .
Our Application (IIQ 8.1) Server is Apache Tomcat hosted on AWS EC2 along Database server(AWS RDS -SQL Server 2019).
We would like to understand the recommendation for above mentioned SailPoint deployment as we are seeing performance issues.
Any help here would be appreciated.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Content to Moderator
Thank you for this insightful article. Based on the information from the Solved: MS SQL Server in Detail - Compass (sailpoint.com), I believe it's acceptable to proceed with AlwaysOn in synchronous mode for high availability, provided the database instances are on the same subnet with minimal latency. Our DBA is also recommending AlwaysOn with failover, but we are hesitant after reviewing the information above.
Could you please advise on any recent improvements? Also, what is recommended for SQL Server DB high availability in a setup where we have 2 UI and 2 task servers pointing to the same database?